No one can understand the value of good SEO better than a digital marketer or a search engine optimizer can. If you don’t have SEO experts in your marketing team, how would you kick-start your first SEO campaign?
In this post, you’ll learn how to optimize your website, create SEO-friendly content, and drive greater traffic to your site. But first, here are some things that you need to keep in your mind:
- Don’t establish your business success on your site’s SEO.
- Google does what it does, what matters is that what you do on your website.
Get a sneak peek at the source code
When considering the source code on any web page, remember that it’s just a set of codes that your user’s web browser would read to exhibit your site’s content in an organized way. Google and all other search engines go through your source code to discover your services and offerings.
To view the source code, try these keys:
For PC users: CTRL + U
For Mac users (chrome): view -> Developer -> view source
Check the Title Tag
In case you are not familiar with it, title tags are the HTML elements, specifying your web page’s title. They can be seen on SERPs (search engine results pages) as the clickable title for a certain result, and are essential for usability, social sharing, and SEO.
Press ‘CTRL + U’ on any of your web page to see the title tag in its source code. Make sure that there is only one title tag on a page. What you write as your title tag is actually how the search engine determine what’ll be in SERPs.
Many mentors and experts advise people to place your most important keywords as your tag, but beware! It’s not good to be too keyword-specific. Keep it natural. Just define what your website is all about and write it like a creative head. The more natural your tags are, the better will be its exposure to users.
Meta Description
A meta description is more or less a piece of code that is placed in the header of a page. You have only one meta title on one page. With every title comes a description of the page. You can use this description to enlighten your web site visitors what your web page is all about descriptively. Your meta data can be seen in the search engine results and therefore they matter a lot. It is free advertising provided by Google. Your audience and prospects are going to read it before clicking on your link.
H1 HeadingTag
It is the main heading of your web page. Try to keep it creative and catchy. It should be inviting enough to lure the website visitors once they click through and skim your website content. It works really well in setting up the visitor’s mind to reading your content further. Some people just use their key phrase or the title tag content in their page’s H1 which is not wrong, but try to go for something a bit more engaging and more specific; come up with something that makes more sense for your users. Google considers H1 seriously, so don’t try to stuff your keyword in this page. Keep it natural and engaging.
Internal Links and Anchor Text
An important basic is how internal links and anchor texts work. On any web page, you’ll have links to any content. This is what the code looks like for any link.

This can go to a link on your site or a link to another website. Another important thing is that the content nested by this tag is the anchor text. In the example above, “This is a link to my website.” is the anchor text. The words in the anchor text are a very important thing that search engines pay attention to. It helps them figure out what that page is going to be about and they use it in their algorithm to understand what your entire site is about and what pages they should serve to their users. A lot of people used keyword-stuffing this to manipulate it. Remember to make the internal links and anchor text natural and usable.
Nofollow Links
The “Nofollow” Attribute goes inside an anchor link:
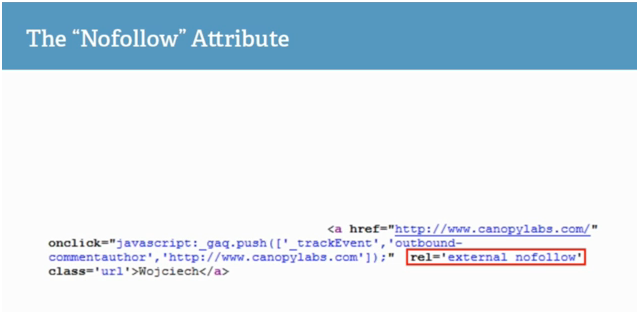
This anchor link is actually a bit more complicated because it has some JavaScript in it, but don’t be too overwhelmed by it. As you can see, Sean has outlined rel=’external no follow’. You can actually just do rel=”nofollow”. The “Nofollow” attribute tells Google and other search engines not to follow the link to the next page and not count it as link juice. You’re hugging up your page with no follows if you use them. You’re saying that you don’t want Google to focus on the next page. You want to direct Google towards things that you think are more important.
You should really only use this for comments in blogs to keep blog comment spam down because oftentimes people leave links to other sites. The “Nofollow” tag was created to keep these spammy users at bay. In the past, people used to like the “Nofollow” tag to page sculpt, which means you try to direct your link juice to certain parts of the site that they really want you to focus on. You should abstain from doing this practice and just use it for editorial purposes and in your blog comments. For more information on nofollow and when to use it, check out Google’s documentation.
Image Alt Tags
The Image Alt tag is another tag that is extremely important, especially if you’re in eCommerce.
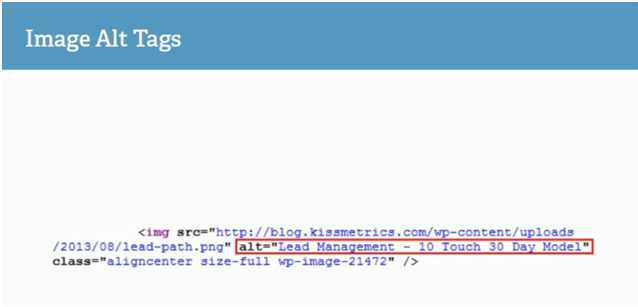
What this does is that it tells a search engine what an image is about. As you can see in the example, the image is about lead management. This is how robots like Google know what your image is about and it helps your image become higher in the image search.
Don’t use ‘Image Alt’ tags for decorative images. Use them for:
- Images of merchandise
- Diagrams
- Infographics
- Your website logo
- Screenshots
- Photos of team members
…and other places where it’s appropriate usage. Think of your ‘Image Alt’ tag this way: If you had to describe your image to a blind person, how would you describe it?
Canonical Tag
The Canonical Tag is a very important tag that came out relatively recently:
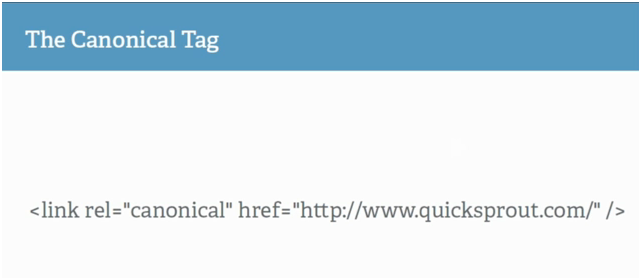
It’s important because if you have a lot of web pages that have similar content, you can tell Google that the only page they should page attention to is a certain page. This is a good way to stop duplicate content. This is also important to syndicate your content, as you can have people who syndicate your content use this tag in their head of their page that they’re taking from you and pointing back to you as the original source. In essence, canonical tags are useful for setting a preferred URL for your content.
Now that you know the different tags and how they are important for SEO, watch the rest of the webinar to learn how not to get duped by duplicate content and learn about backlinks, content and user experience (UX).
 Latest Digital Marketing Trends
Latest Digital Marketing Trends





Thanks so much. We are just starting our SEO journey, so this comes in handy. We have a ways to go and we’re having a meeting to discuss process next week.
Thanks for this quick and to the point guide on how to optimize via source code. I have seen a lot of posts about this but this one makes it easier to understand.
I think for wordpress users yoast is the best plug to manage seo of a websites.